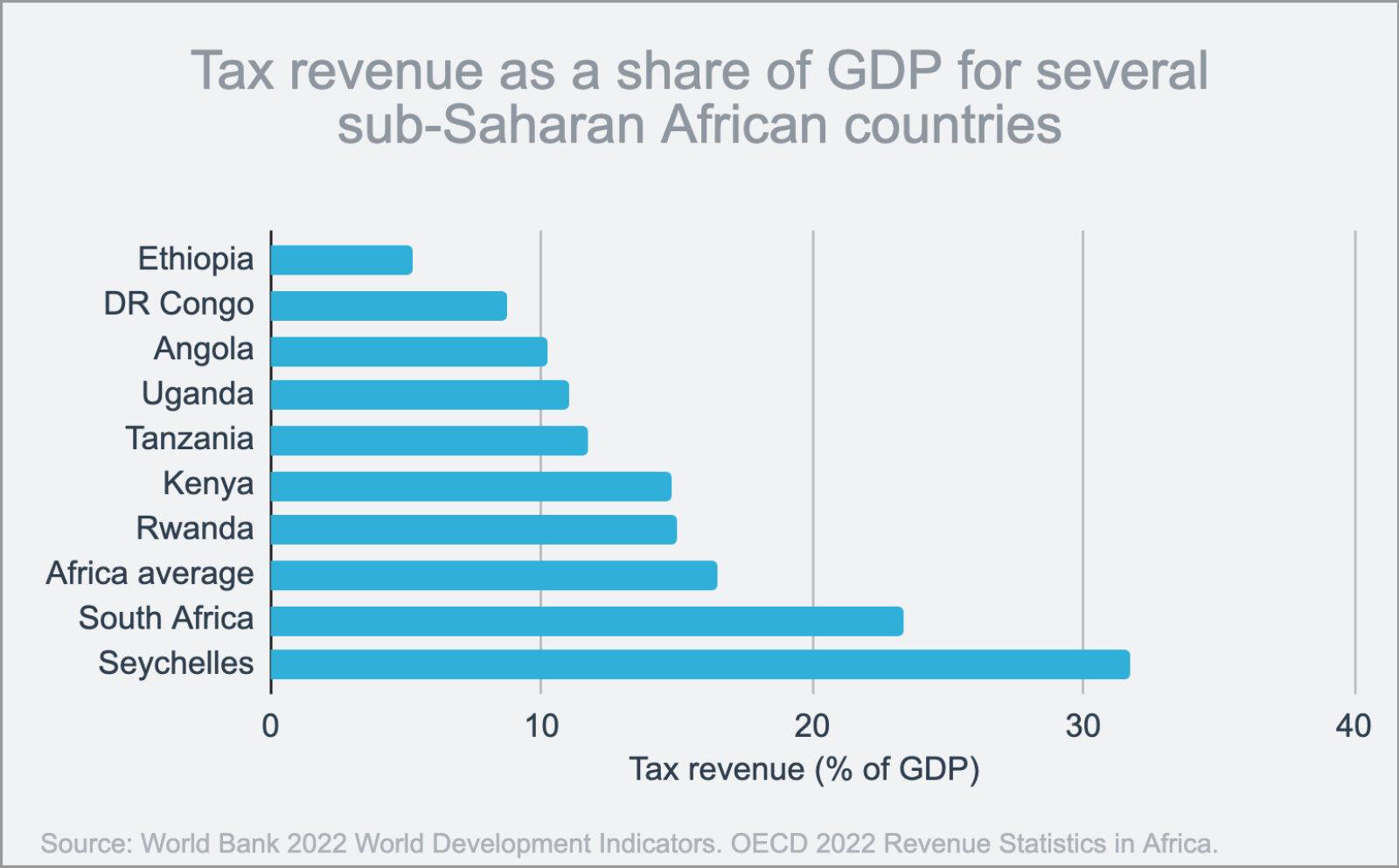
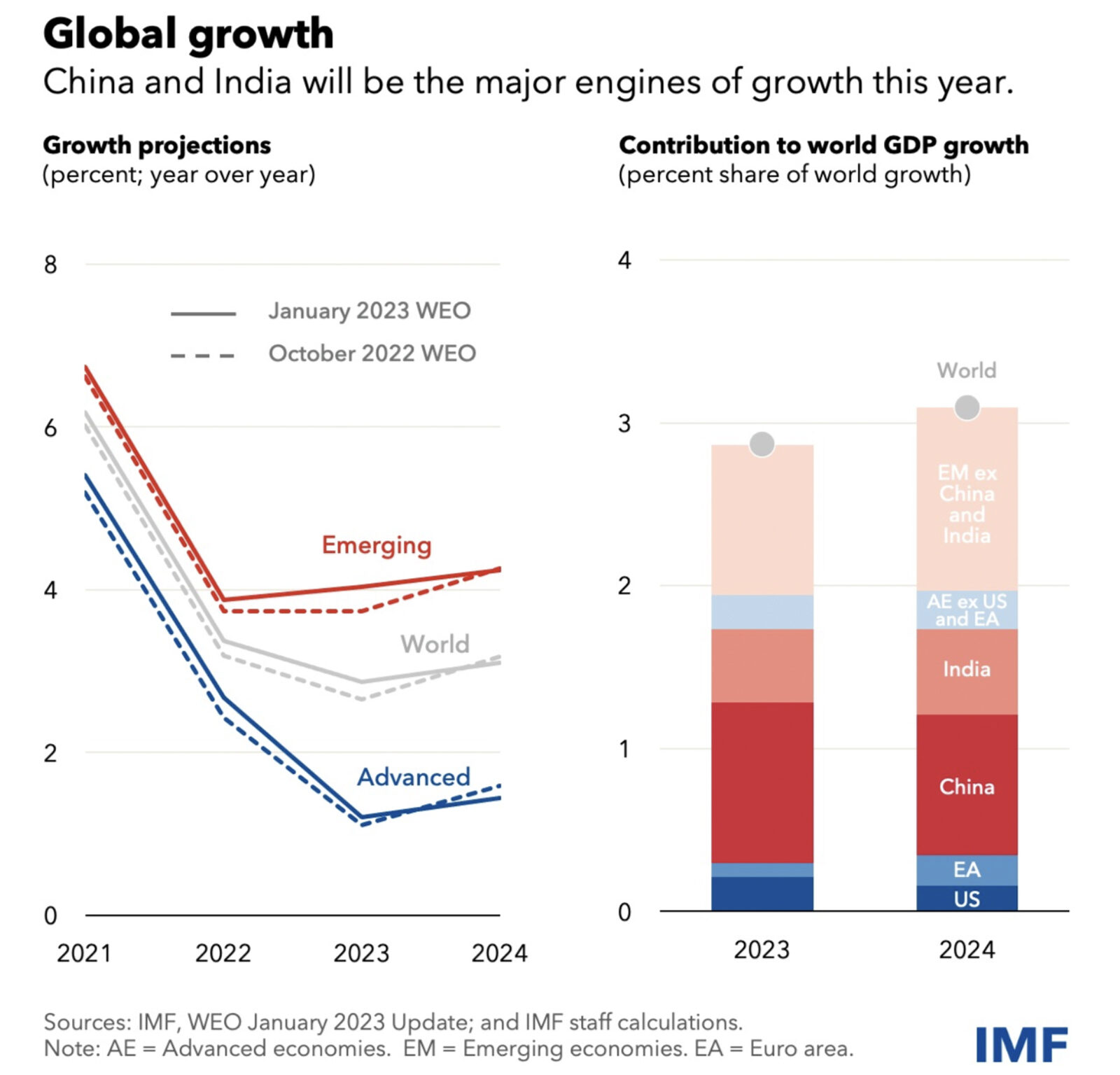
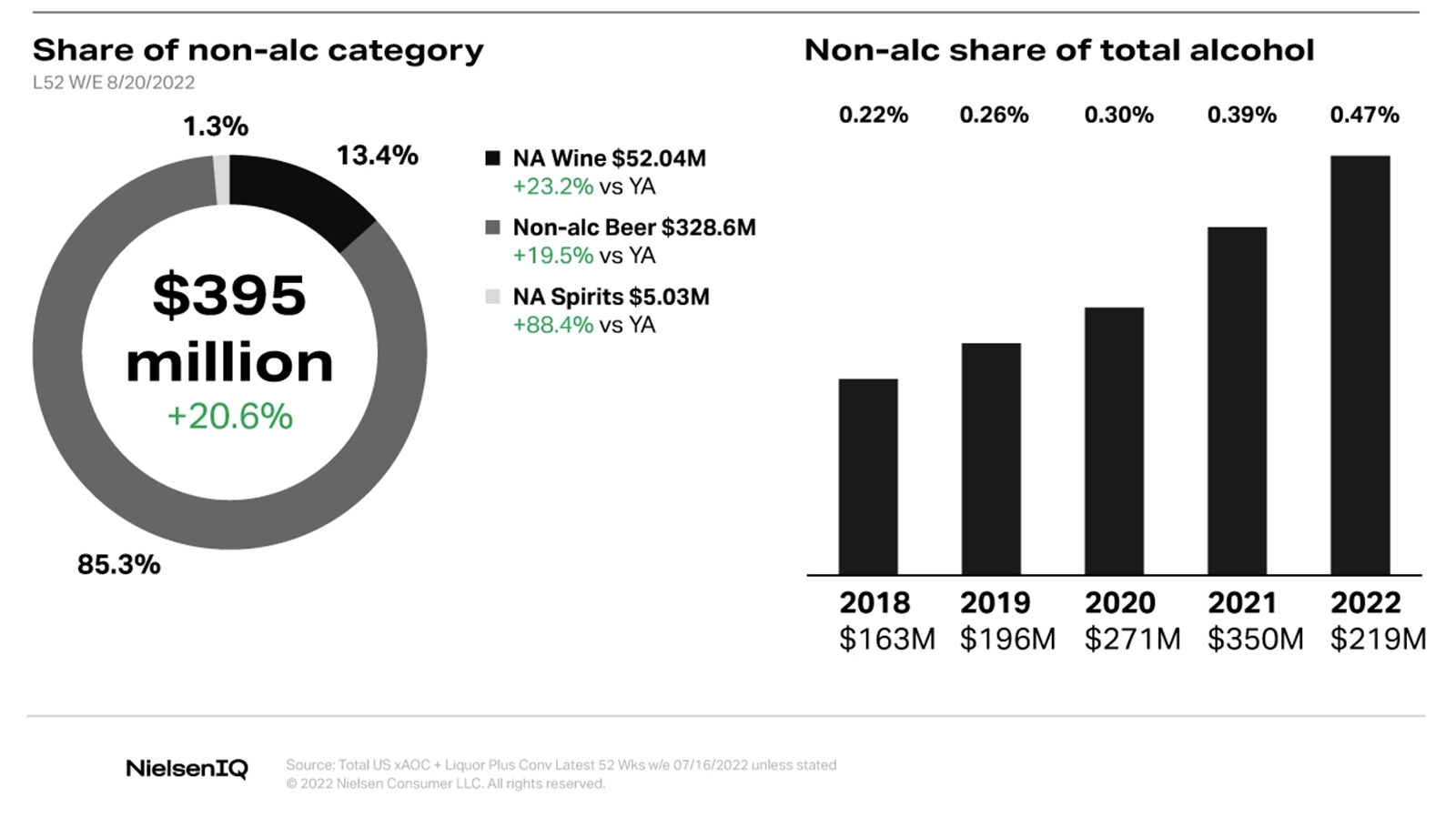
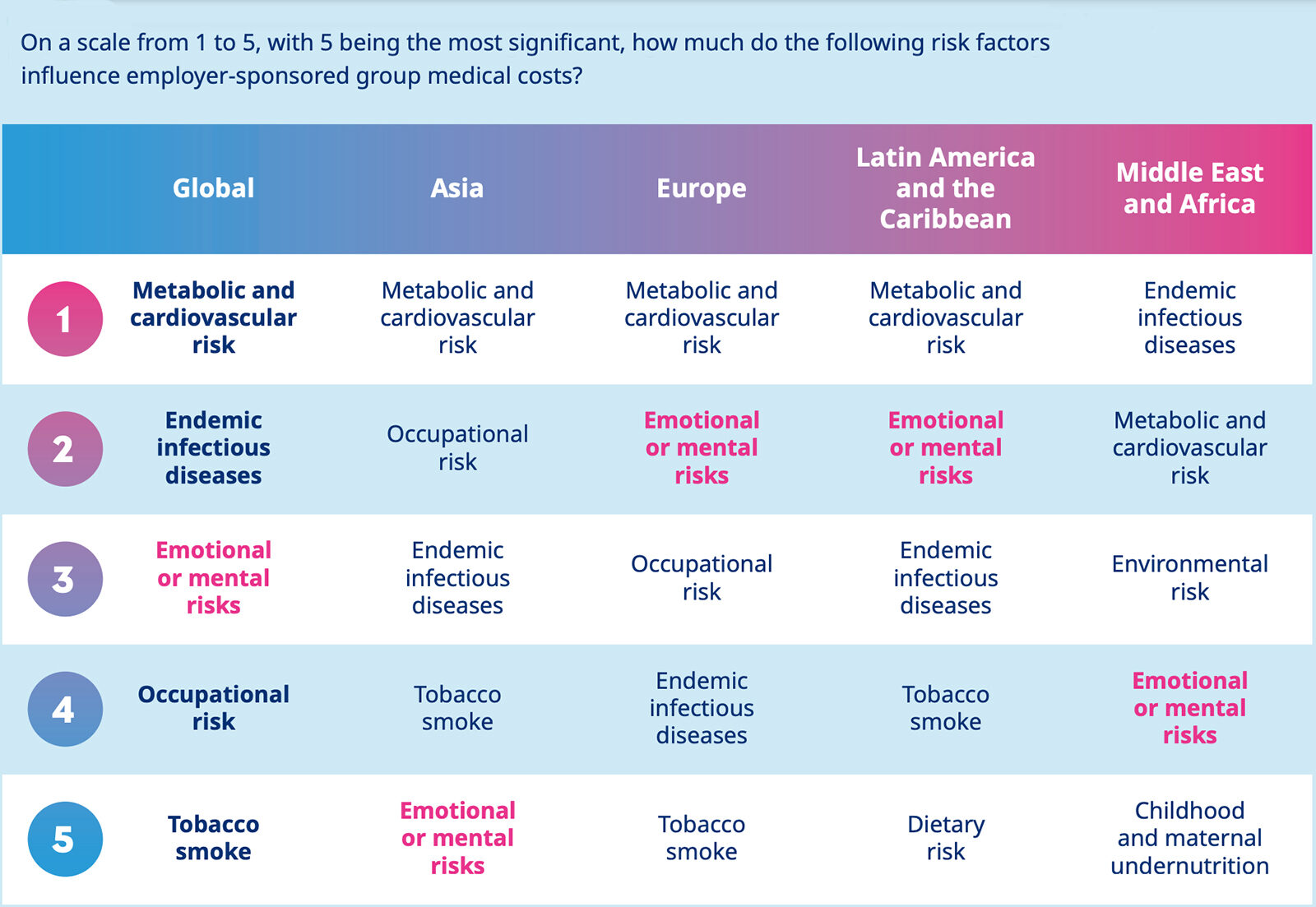
Survey: Younger Generations Losing Interest in Sports
Source: Morning Consult
An estimated 1.5 billion people worldwide watched Argentina beat France to win the 2022 FIFA World Cup in December. Although it was a record viewing for a World Cup final, younger sports fans and their viewing habits are changing.
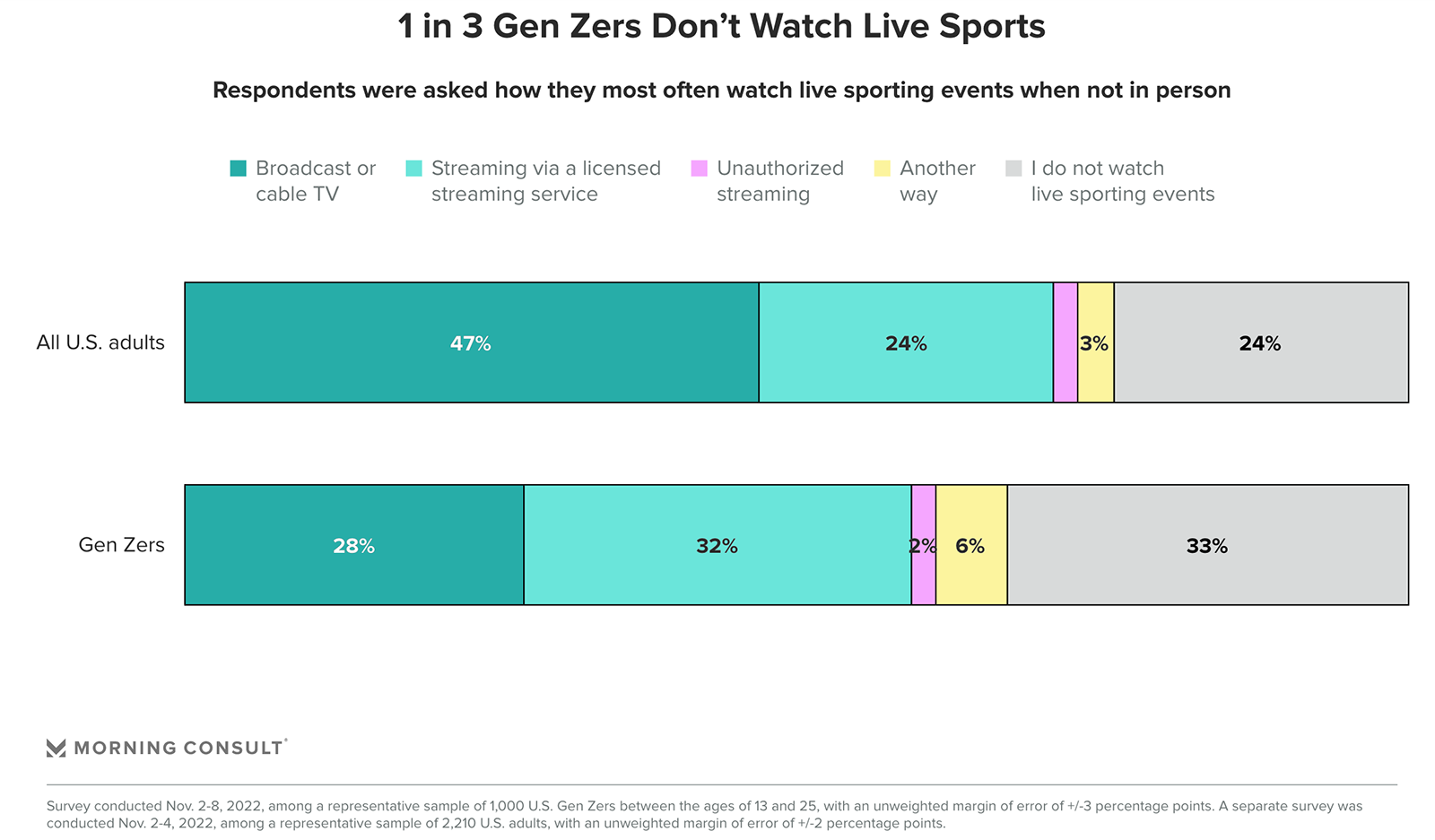
A new survey from Morning Consult found that Gen Z consumers in the U.S. are watching less live sports than the group of “all U.S. adults” — on broadcast TV, streaming services, or any other platform. A third don’t watch any live sports at all, compared 24% of all U.S. adults who said they don’t watch live sports.
Fandoms also appear to be shrinking, with 38% of Gen Z responding that they do not support a particular team, versus 28% of all American adults.
“The struggle for sports to latch on with Gen Z, relative to their older counterparts, is exacerbated by the multitude of other readily accessible entertainment options, the popularity of established and emerging social media platforms, the fragmented nature of sports media rights distribution, accessibility to games and ticket affordability,” the report states.