Climate Summit Leaders Set Out Largest Emissions Cut Since 2015
Source: CAIT, Climate Action Tracker, Marsh McLennan Advantage
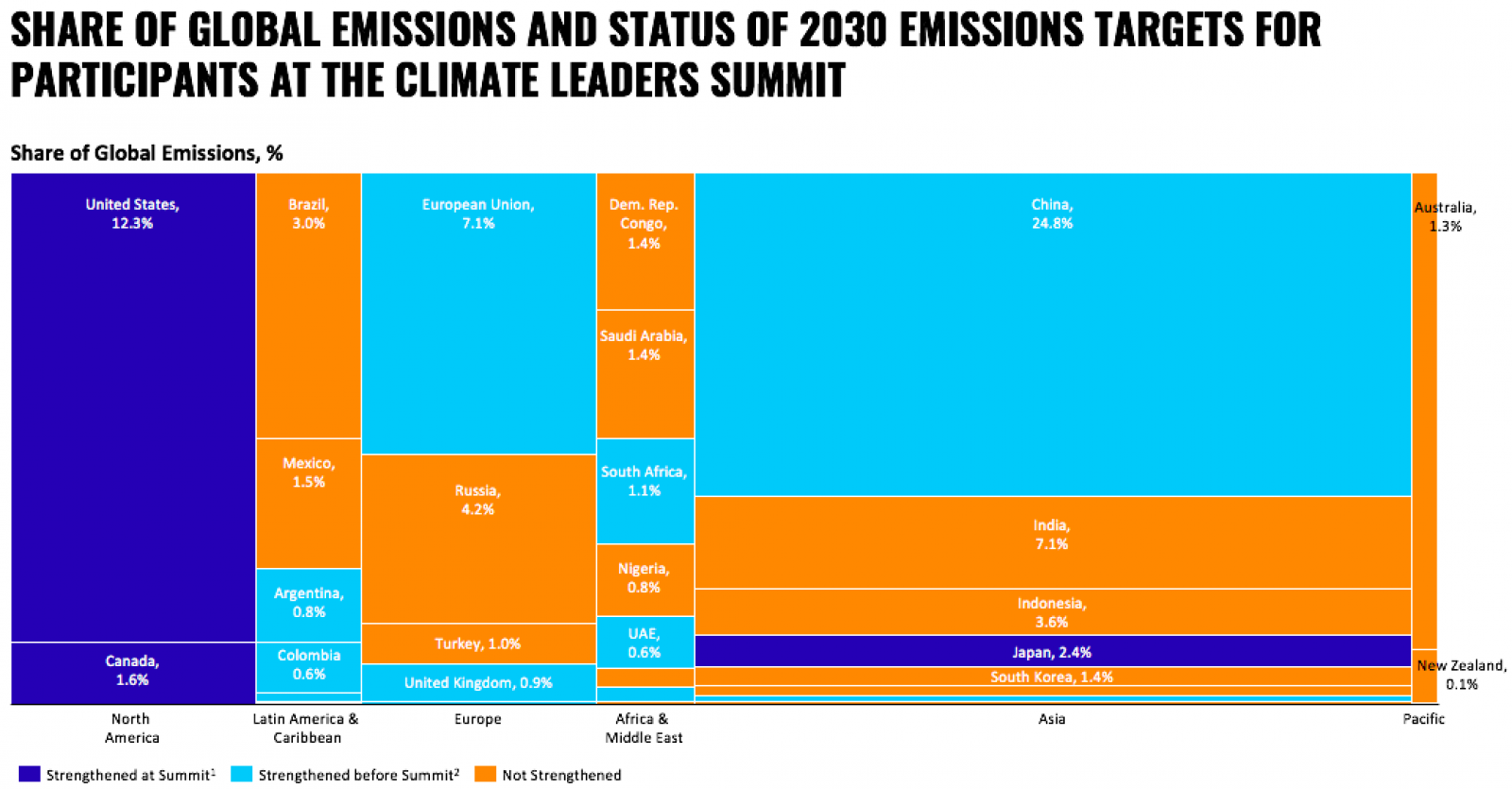
Note: 34 parties including the U.S. were analyzed from the 40 World Leaders invited to the Leaders Summit on Climate. Leaders from the European Commission, European Council, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Poland, and Spain were aggregated into one party—the “European Union”—for analysis. Total emissions data from 2018 was used and includes Land use, land-use change, and forestry (LUCF) and all greenhouse gases (CH4, CO2, F-Gas, N2O, etc.). Other parties not listed make up 1.9% of global emissions including, Chile, Jamaica, Antigua and Barbuda, Norway, Israel, Kenya, Gabon, Vietnam, Bangladesh, Singapore, Bhutan, Marshall Islands. The horizontal length of each region in the chart represents the share of total emissions of participants.
The Climate Leaders Summit last week set out the single biggest reduction in the global emissions gap since Paris, shaving off around two gigatonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent from 2030 emissions. (See footnotes 3 and 4 below.) Nevertheless, the emissions gap remains enormous — with around 29 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent left to address before the world can be on a 1.5 degree-Celsius pathway.
The summit’s participants are responsible for 81% of global emissions, with the 10 largest emitters accounting for two-thirds of the global total. Their key objective was to announce revised 2030 emissions reduction targets ahead of COP26.
Of those attending, the U.S., Canada and Japan announced new 2030 targets. The U.S. pledged to reduce emissions by 50-52% below 2005 levels by 2030 and is responsible for almost 80% of the combined 2030 savings pledged at the summit.
1. Announced plans to strengthen NDC at Leaders Summit on Climate. 2. Strengthened or announced plans to strengthen NDC before the Summit. 3. For the calculation of US emission savings, we assumed for the baseline, the emissions reduction trend from 2025 to 2030 would have been a continuation of the 2005-2025 trend. 4. For countries which proposed a new emissions reduction target range, the midpoint was used.