Home Ownership Is Set to Plummet, and Social Safety Nets Are Not Equipped for the Fallout

A real estate agent puts a 'sold' sticker over advertising signage in Sydney, Australia. The share of people in Australia over 65 who own their home will fall from 76 percent today to 57 percent by 2056.
Photo: Torsten Blackwood/AFP/Getty Images
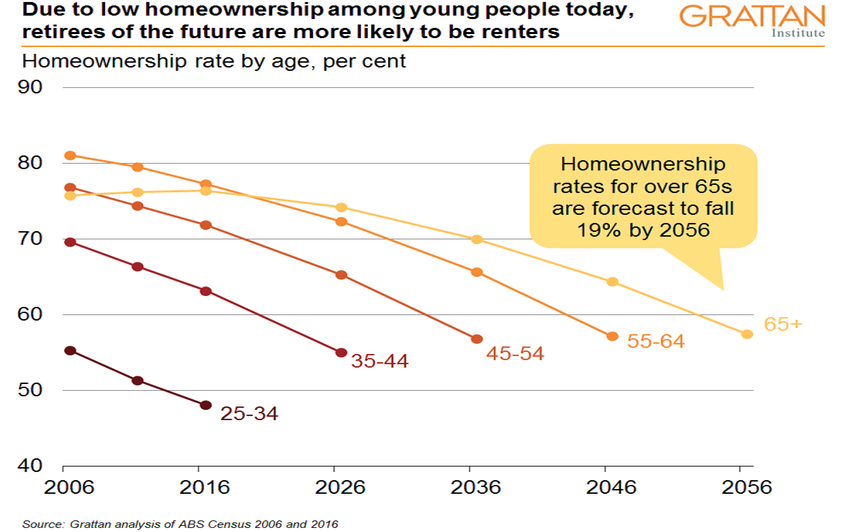
Australia’s retirement income system has relied on the assumption that most retirees would own their home outright. But new Grattan Institute modeling shows that the share of people over 65 who own their home will fall from 76 percent today to 57 percent by 2056—and it’s likely that fewer than half of low-income retirees will own their homes in future, down from more than 70 percent today.
Home ownership provides retirees with big benefits: They have somewhere to live without paying rent, and they are insulated from rising housing costs. Retirees who have paid off their mortgage spend much less of their income on housing (on average 5 percent) than working homeowners or retired renters (25-30 percent). These benefits—which economists call imputed rents—are worth more than $23,000 a year to the average household aged 65 or older.
Renters Face Challenges That Homeowners Do Not
Our 2018 report Money in Retirement showed that while Australia’s retirement income system is working well for the vast majority of retirees, it’s at risk of failing those who rent. They are more than twice as likely as homeowners to suffer financial stress, as indicated by things such as skipping meals or failing to pay bills.
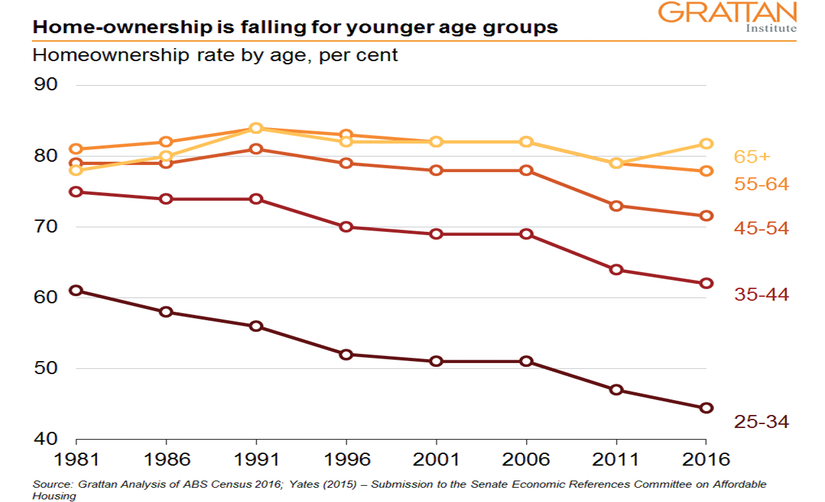
This is not surprising: Renters typically have lower incomes. But the rising down payment hurdle and greater mortgage burden risks means rates of home ownership are falling fast among the presently young and the poor.
The share of 25- to 34-year-olds who own their home has fallen from more than 60 percent in 1981 to 45 percent in 2016. For 35- to 44-year-olds it has fallen from 75 percent to about 62 percent.
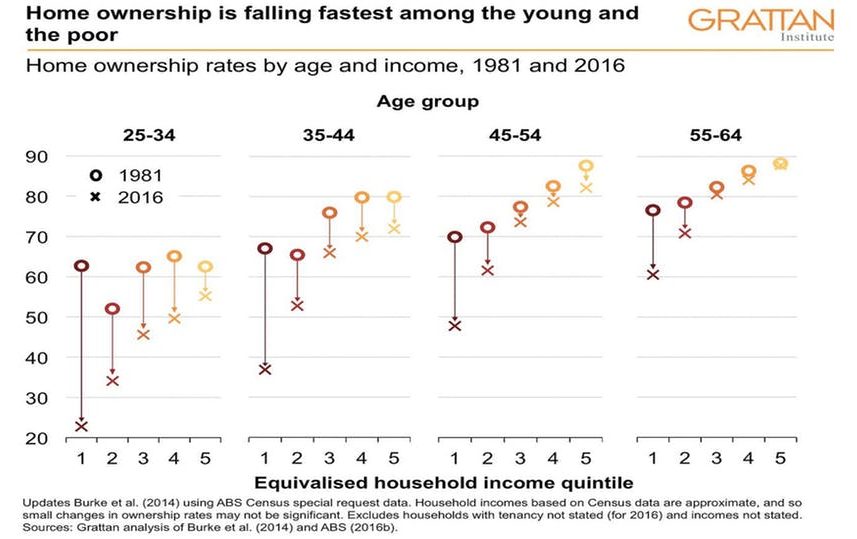
Home ownership now depends on income much more than in the past: Among 25- to 34- year-olds, home ownership among the poorest 20 percent has fallen from 63 percent to 23 percent.
Home ownership is likely to fall further in coming years. Using Grattan Institute modeling, we find that on current trends, the share of people over 65 who own their home will fall from 76 percent today to 74 percent in 2026, to 70 percent by 2036, 64 percent by 2046, and 57 percent by 2056.
While we don’t project home ownership rates for different income groups due to data limitations (we have the necessary Census data on home ownership rates by age and income only for 1981 and 2016), it is more than likely that less than half of low-income retirees will own their homes in the future, down from more than 70 percent today.
Today’s younger Australians will be tomorrow’s retirees. But worsening housing affordability means renting will become more widespread. As a result, more retirees will be at risk of poverty and financial stress, particularly if rent assistance does not keep pace with future increases in rents paid by low-income renters.
Rent Assistance Won’t Help Much
The maximum rent assistance payment is indexed in line with the consumer price index, but rents have been growing faster than the consumer price index for a long time. Between June 2003 and June 2017, the consumer price index climbed by 41 percent, while average rents climbed by 64 percent.
That’s why our report recommended boosting Commonwealth Rent Assistance by 40 percent, at a cost of $300 million a year in today’s dollars. That would restore the assistance to the buying power it had 15 years ago. It should also be indexed in the future to changes in the rents typically paid by the people who receive it, so its value is maintained, as recommended by the Henry Tax Review.
There’s another important implication. Money in Retirement found that, in general, future retirees will have adequate retirement incomes. Most workers today can expect a retirement income of at least 89 percent of their pre-retirement income, well above the 70 percent benchmark used by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, and more than enough to maintain pre-retirement living standards. But retirees who rent will have much less to live on.
The ‘Haves’ and ‘Have Nots’
Among homeowners, an increasing proportion will be still paying off their mortgages when they retire: the proportion of 55 to 64 year olds who own their home outright fell from 72 percent in 1995-96 to 42 percent in 2015-16. Some will (quite rationally) use some or all of their superannuation to pay off their mortgage.
And rising housing costs will in time force retirees to draw down on more of the value of their home to fund their retirement.
Currently, few retirees downsize or borrow against the equity of their home while continuing to live in it. But that will have to change.
House prices have outstripped growth in incomes. Median prices have increased from around four times median incomes in the early 1990s to more than seven times median incomes today (and more than eight times in Sydney).
Government policy should continue to encourage these retirees to draw down on the increasingly valuable equity of their homes to help fund their retirement. They are not the ones who will need government help. The government’s recent expansion of the Pension Loans Scheme that allows all retirees to borrow against the value of their homes is a step in that direction.
Retirement is going to change in the years ahead. Most retirees will be far from poor, many of them better able to support themselves than ever before. But an increasing number will not. They are the ones who will need our help.
This piece first appeared in the Conversation.