COVID Is Forcing Millions Into Premature Retirement
Source: Wall Street Journal
Whether they’re worried about catching COVID, still suffering the long-term effects of COVID, or haven’t found the right job to go back to, Americans who retired early during the pandemic aren’t returning to the labor force.
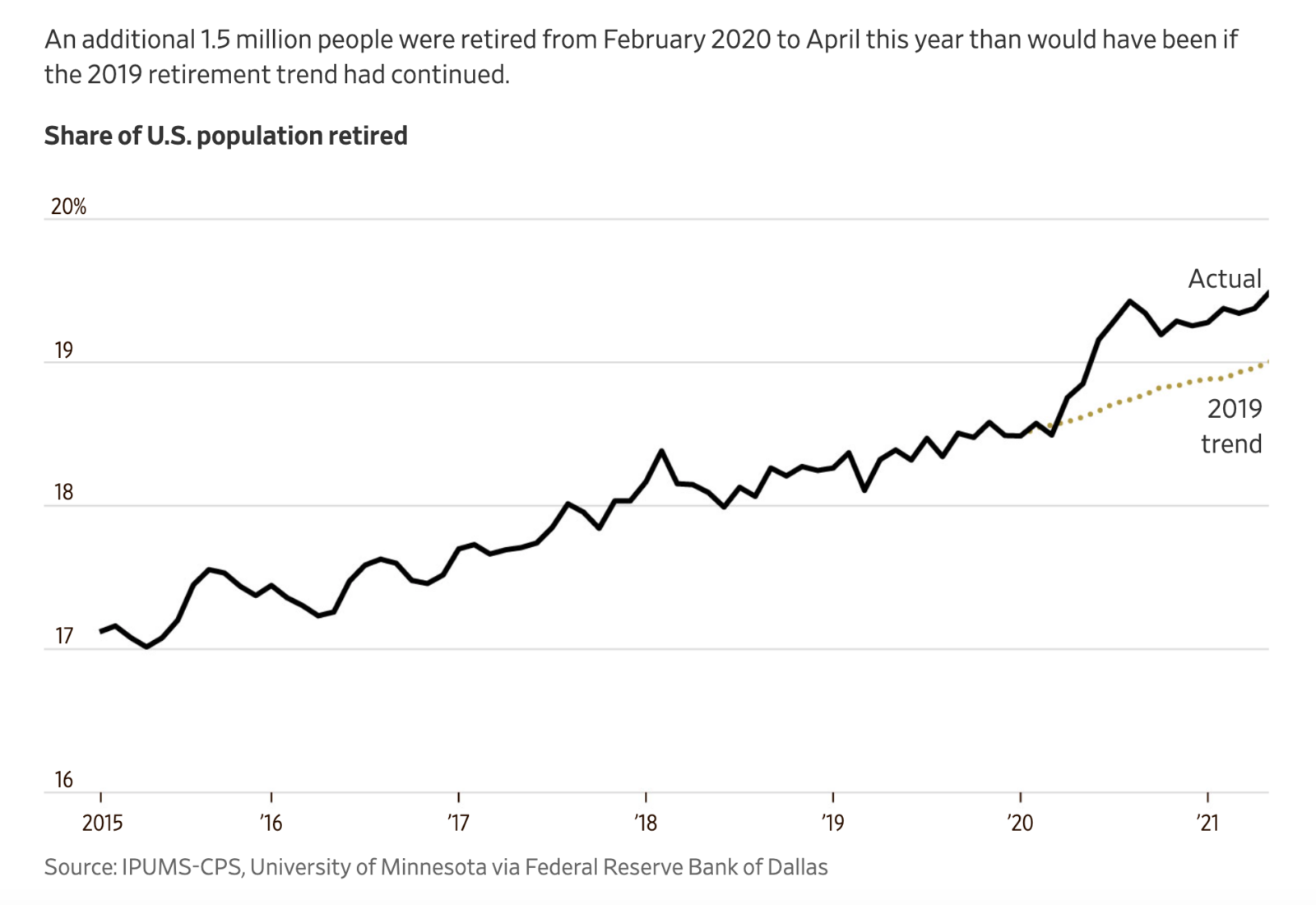
Over the past three months, there have been 3.6 million more people who have left the labor force and don’t intend to return, compared to 2019. Ninety percent of those 3.6 million people are ages 55 and older, reports ABC News. That’s 1.5 million more retirees between February 2020 to April 2022 than predicted by 2019 trends, according to the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas.
Growing concerns over inflation have pushed some workers back into the job market, but the labor force participation rate for Americans 55 and older has remained unchanged from a year ago. In November of this year, baby boomers’ labor force participation rate was 38.6% — nearly identical to their participation rate of 38.4% in November 2021.