Demand for Coal Remains Resilient in Asian Countries
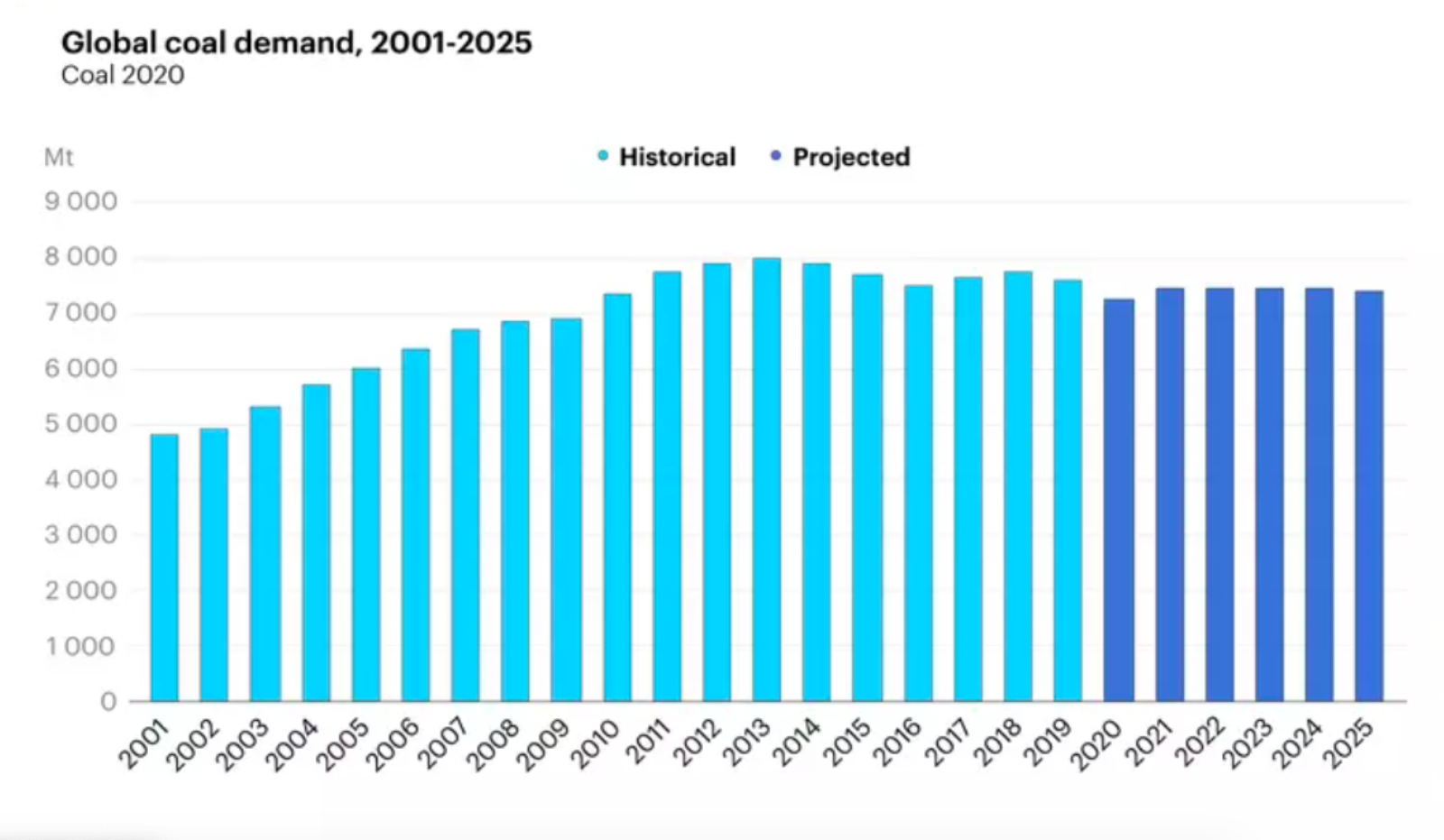
Source: IEA
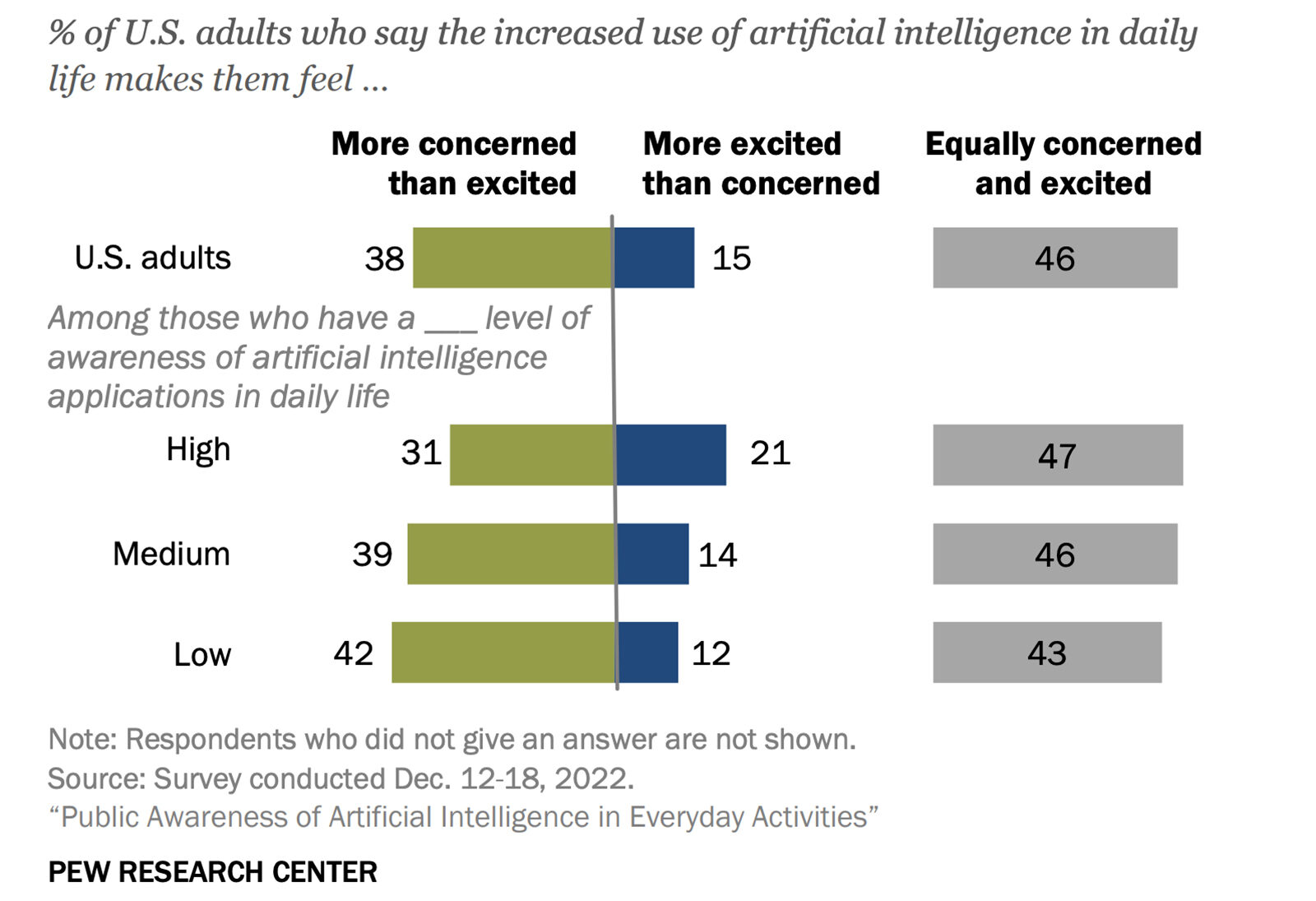
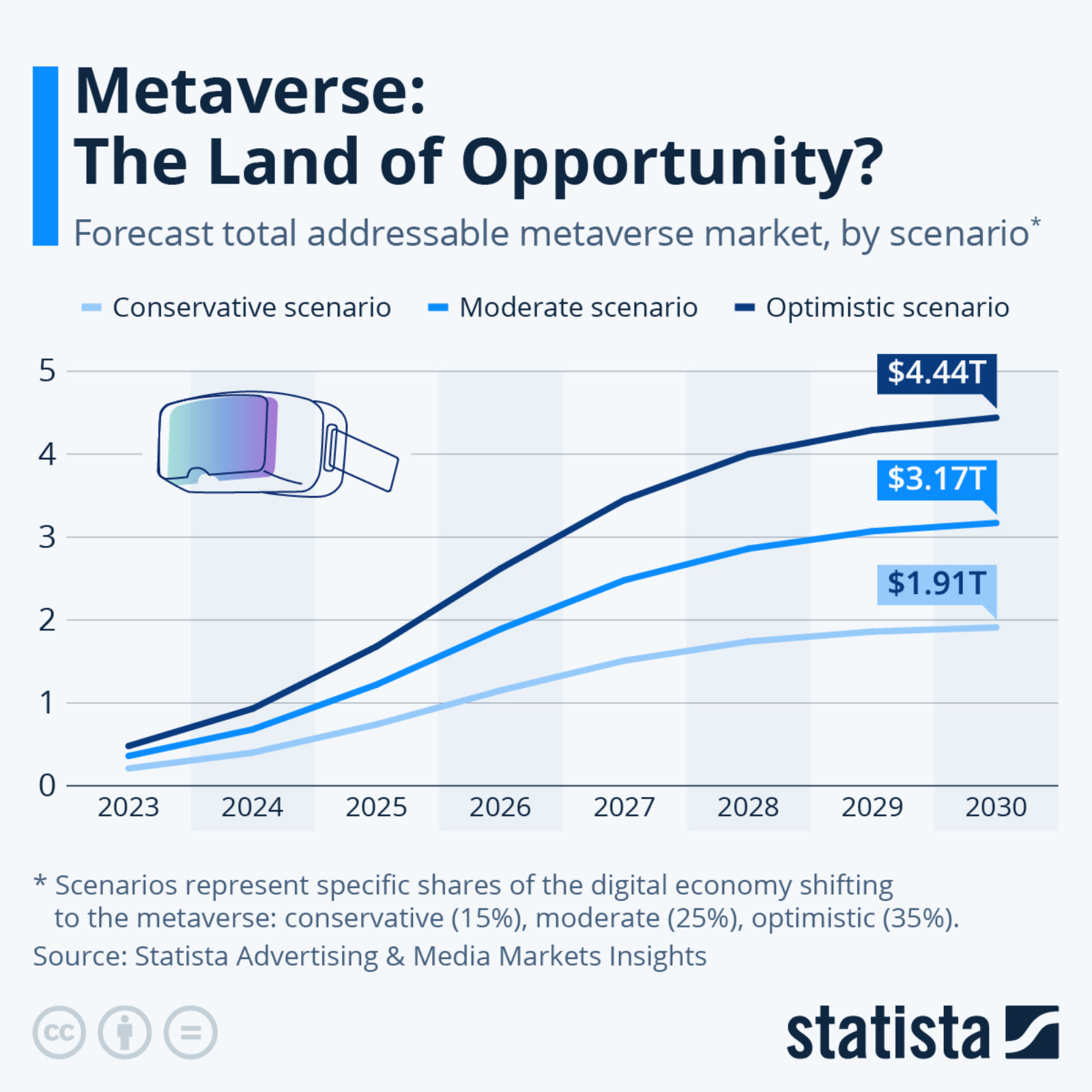
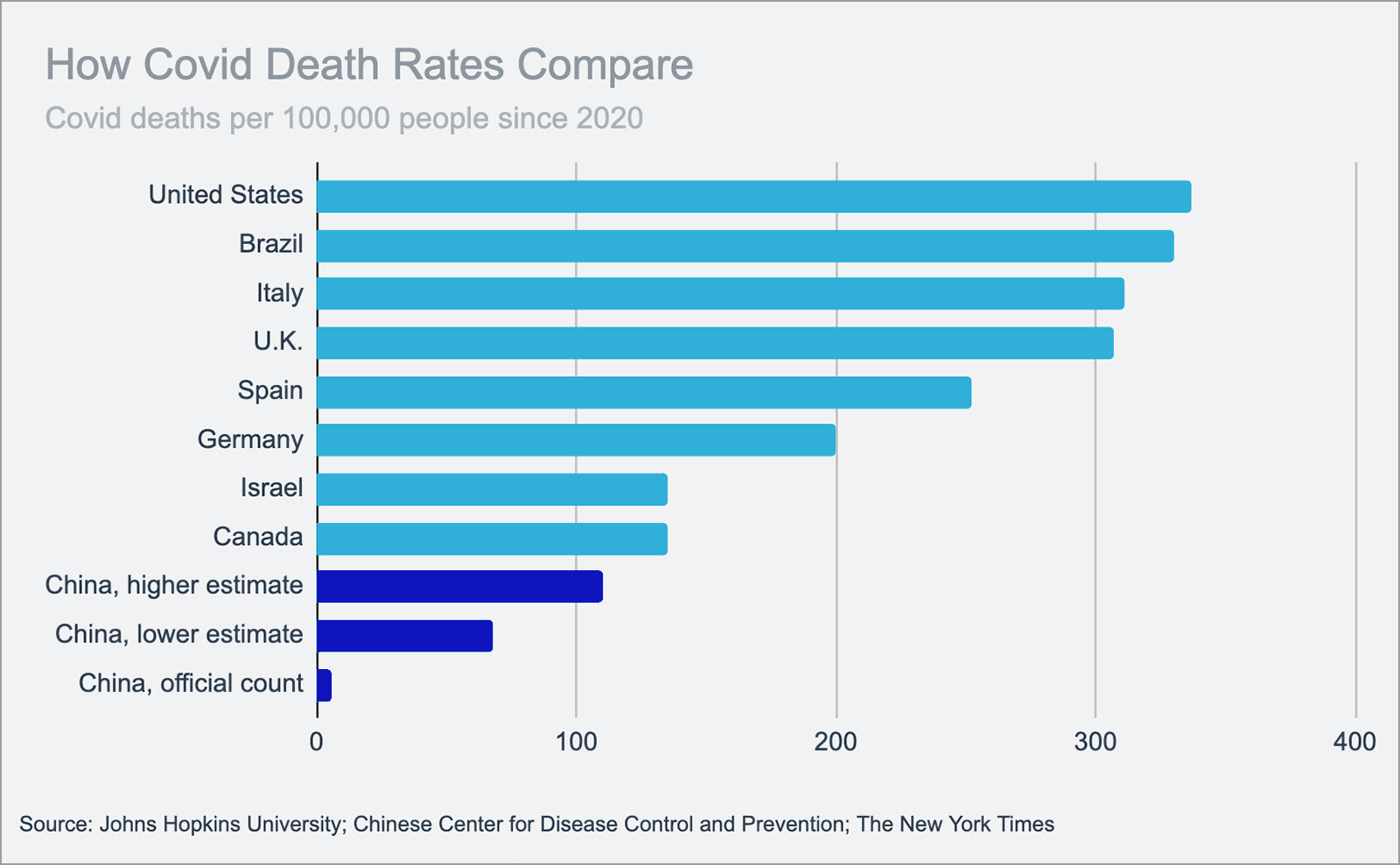
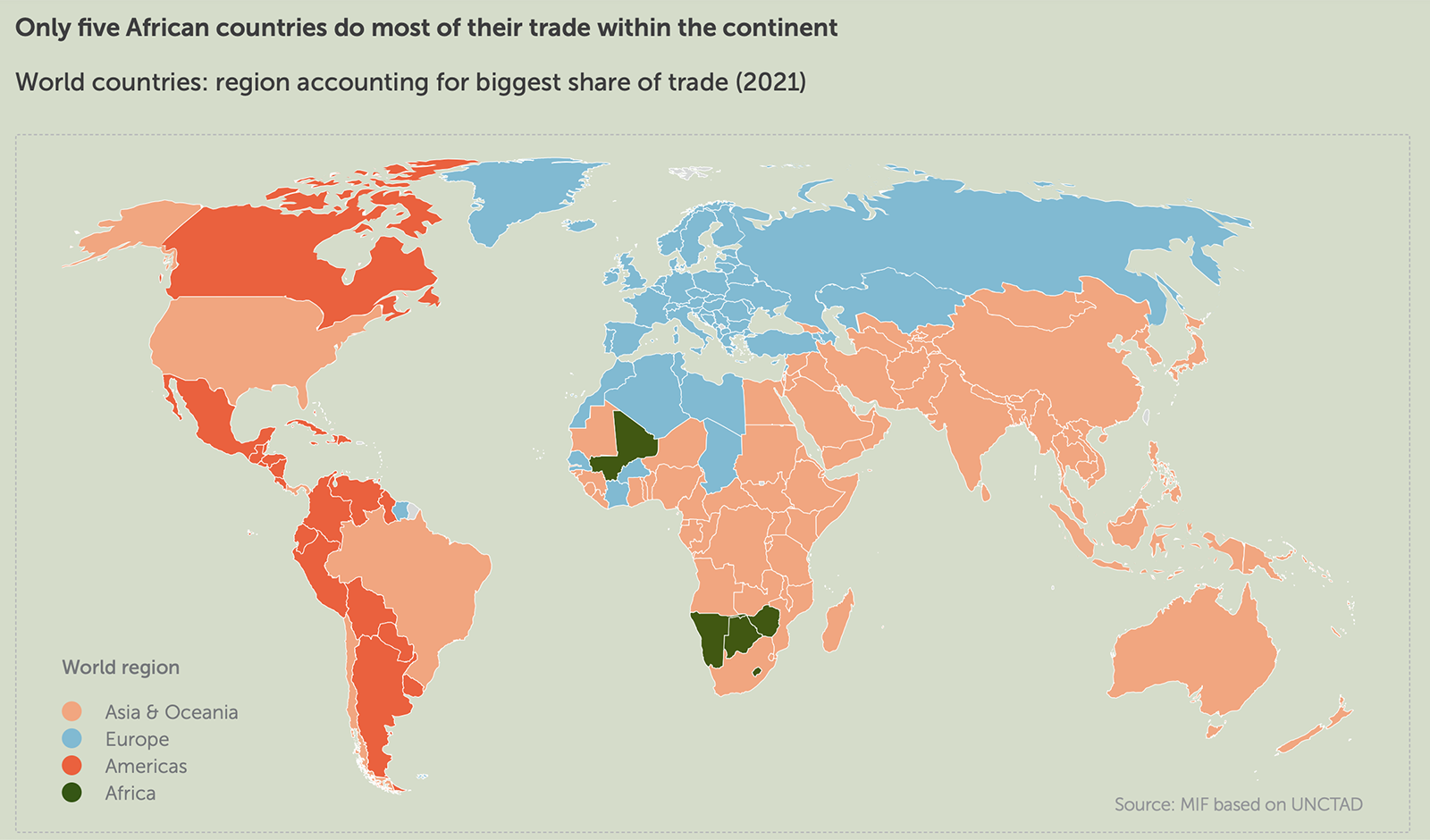
Global coal demand fell 5% in 2020 — the biggest decline since World War II. Europe and the U.S. saw significant declines in demand, but demand for coal in Asia remained steady, according to the International Energy Agency.
Transitioning to renewable energy sources, a major drop in electricity use due to COVID-19 lockdowns and lower natural gas prices all contributed to declining demand for coal in 2020. Whereas demand for coal fell by over 15% in North America and Europe, IEA expects China’s coal use to have declined by less than 1% for 2020. China and other Southeast Asian countries combined account for about 75% of global coal demand.
Despite the negative impact that coal use has on global climate goals, the IEA expects the industry to rebound in 2021 — depending on electricity demand and industrial output post-pandemic. Driven by China, India and Southeast Asia, coal consumption is expected to rise by 2.6% this year.