More Households Turn to Agriculture in Sub-Saharan Africa During COVID-19
Source: World Bank
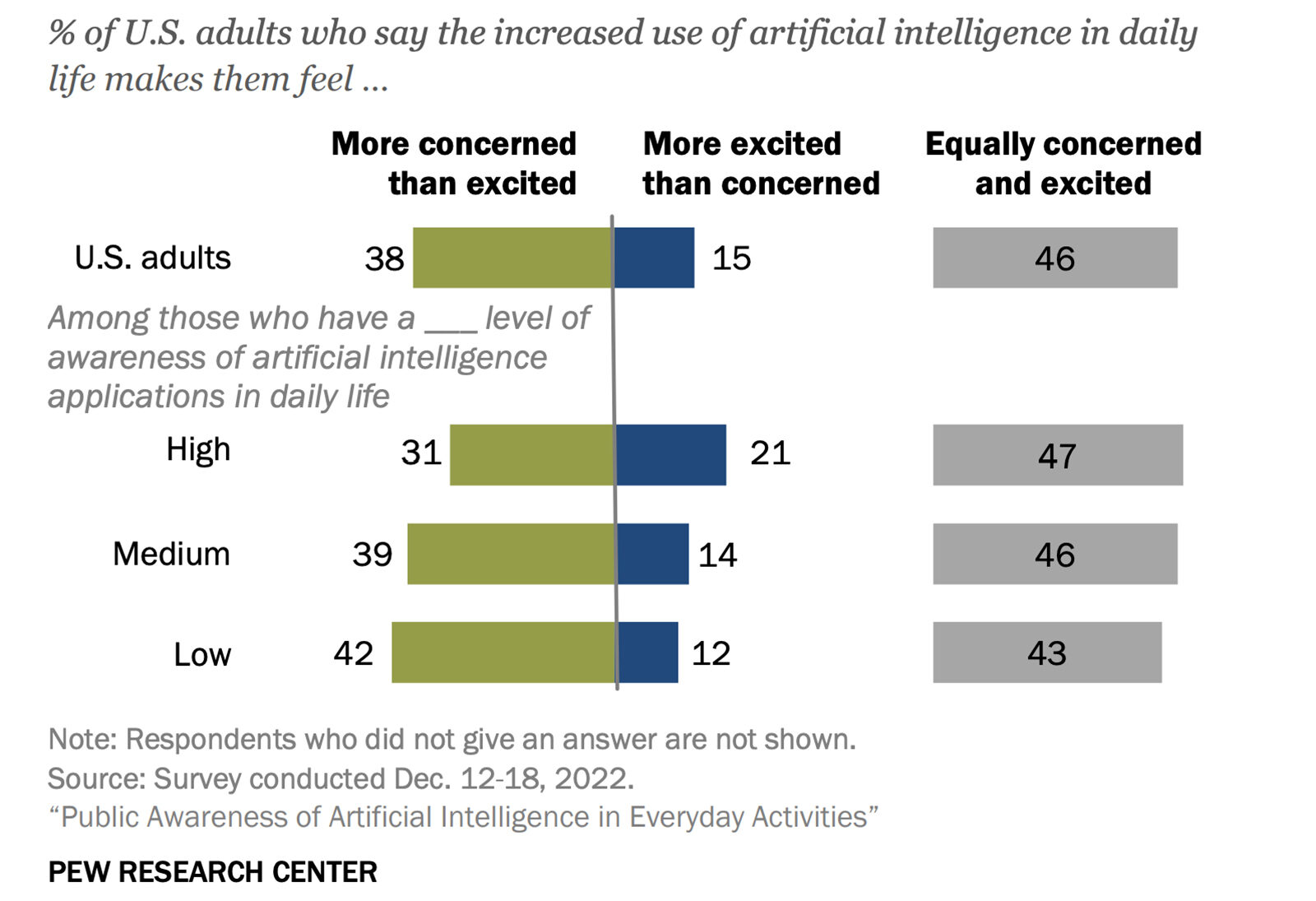
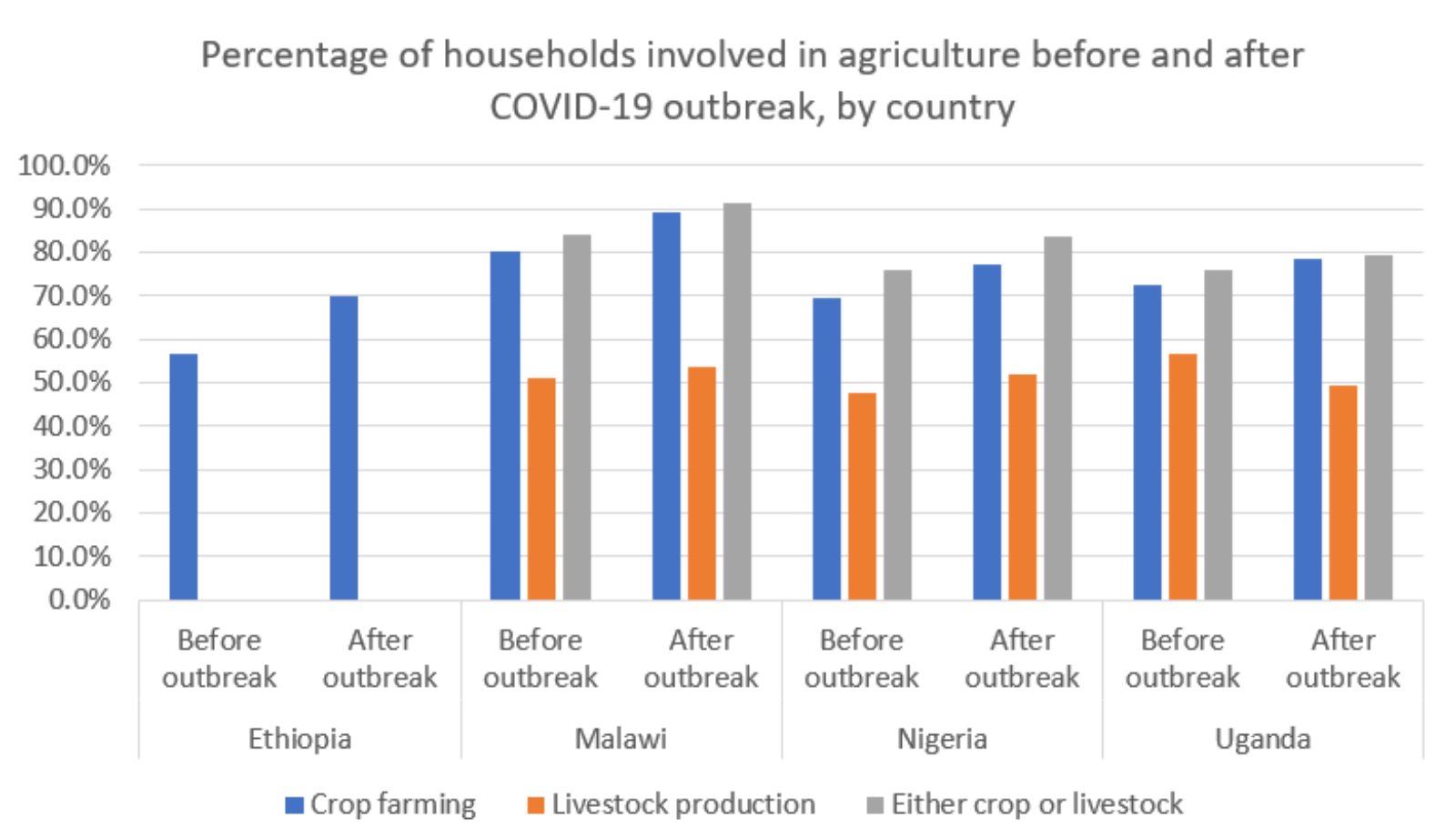
Agriculture was the main source of livelihood for smaller households in sub-Saharan Africa last year. More households entered the industry than exited, and more urban households joined the industry compared to rural households, perhaps due to food insecurity and loss of employment. In Nigeria alone, the percentage of households involved in agriculture increased from 76% to 84% since the start of COVID-19.
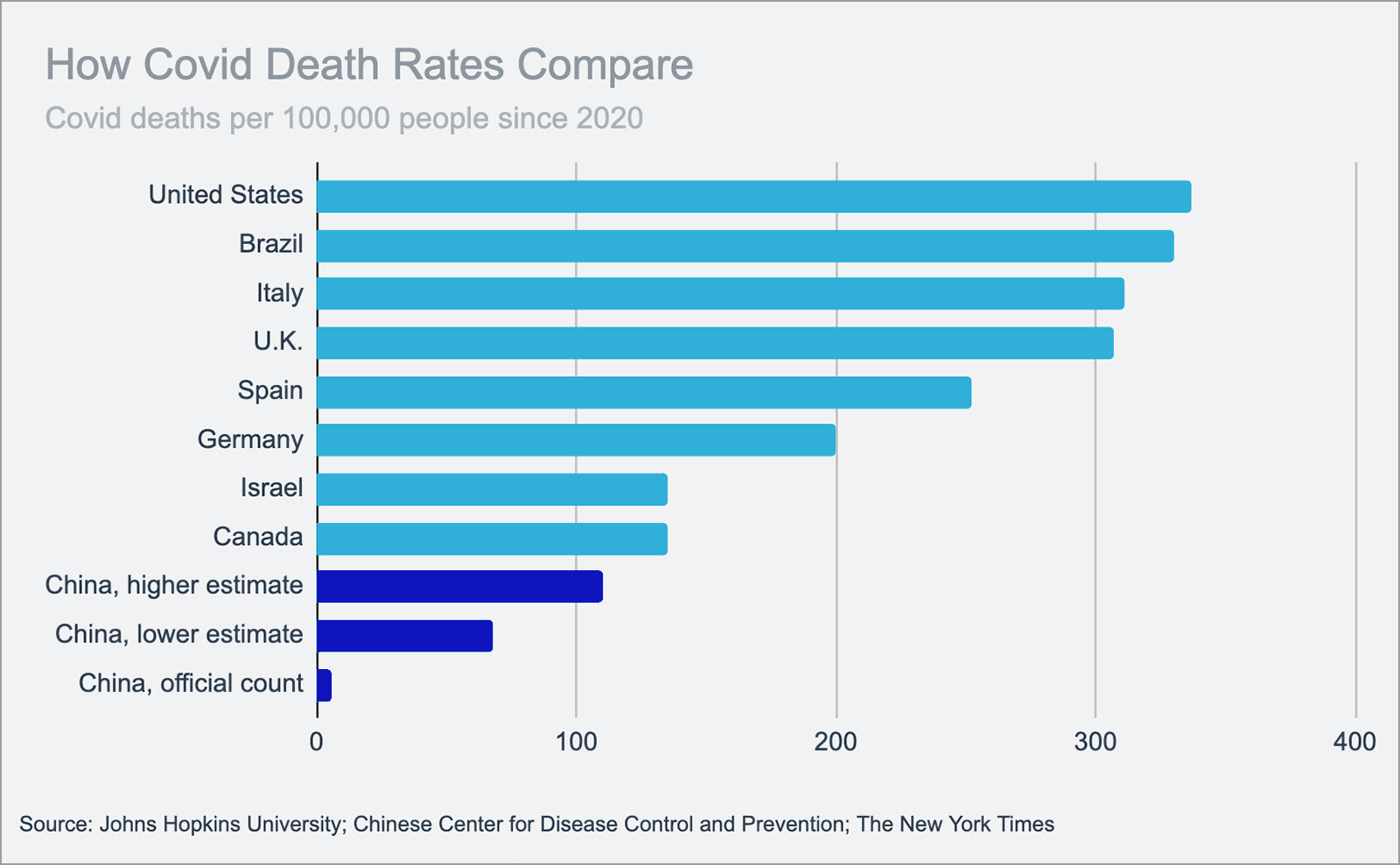
Despite agriculture acting as a “buffer” against COVID-related disruptions, farmers are struggling to access resources, such as feed, animal health services and markets. In Nigeria, 89% of livestock households said they had limited access to feed, for instance, and 82% of households said they had limited access to markets.
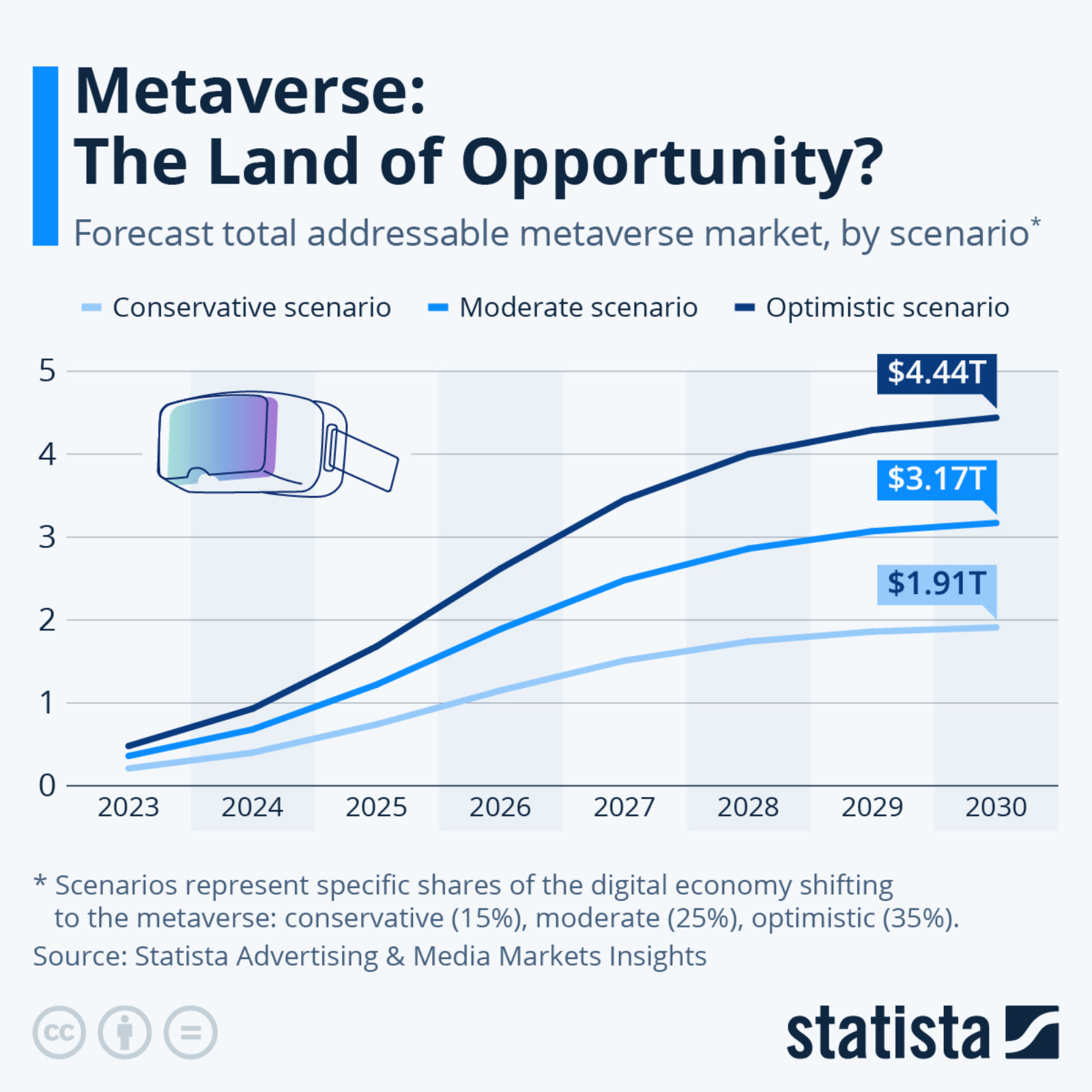
Similar to the 2008 global economic crisis, the agricultural sector absorbed some of the shock from COVID-19 for low-income households in 2020. But moving forward, key stakeholders in the industry will have to address the supply chain disruptions from COVID-19, along with new climate risks.