Russian Invasion Pushes Oil Prices to 10-Year High
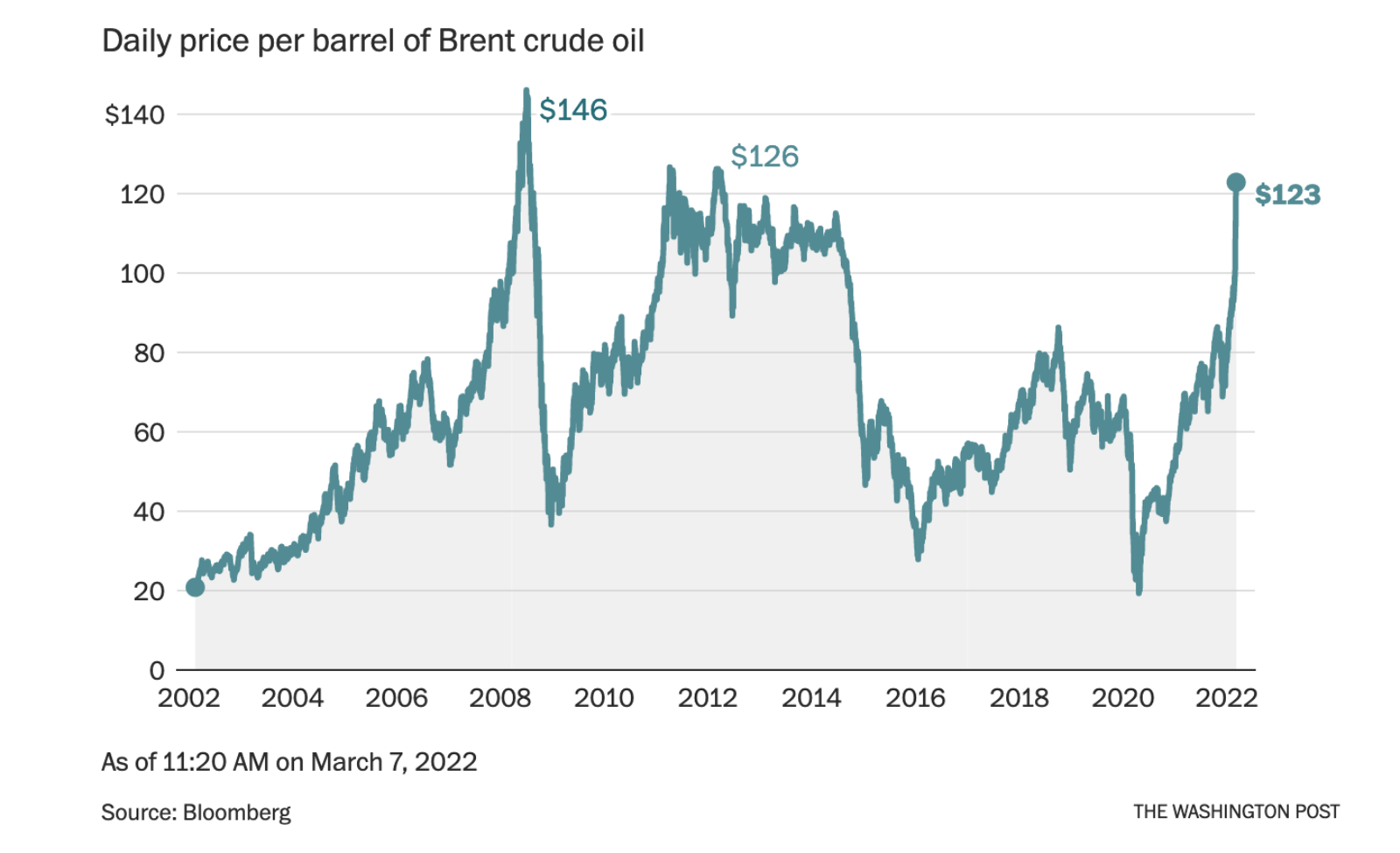
Brent crude, the international benchmark for crude oil prices, rose to $130 a barrel on Tuesday, after the U.S. and U.K. announced a ban on Russian oil imports and the EU said it would cut its dependency on Russian gas by two-thirds this year. West Texas Intermediate crude futures, the U.S. marker, rose to around $125 a barrel.
Global oil prices have risen 58% since the beginning of the year, initially amid concerns about inflation. Russia is the world’s third-largest oil producer, supplying about 7% of global demand. Europe is Russia’s main market for oil and natural gas and bought roughly 25% of its oil from Russia in 2021. Gas prices in the EU have already risen by more than 70% since the last week of February. About 8% of U.S. oil imports came from Russia last year.
The International Energy Agency agreed to release 60 million barrels of oil from its members’ strategic reserves, which is equal to the amount of oil the U.S. consumes in three days. Large Western oil companies like BP, ExxonMobil, and Shell have halted operations in Russia. European refiners are also looking elsewhere for supply, in places like Saudi Arabia. To compensate, Russia is trying to sell crude oil to refineries in China and other Asian countries at a discount.