What the Rise of Female Founders Tells Us About the State of the Gender Gap

Women are starting their own businesses at a faster rate than men since the pandemic, but many in this period likely became “necessity entrepreneurs” as COVID deepened systemic inequalities.
Photo: Getty Images
As we head into a period of economic uncertainty, new data reveals the systemic challenges facing women in the global labor market. Today’s Global Gender Gap Report from the World Economic Forum (WEF) shows that the gender gap hasn’t bounced back from the enormous damage done during the COVID-19 pandemic. The report benchmarks the evolution of gender-based gaps in four areas: economic participation and opportunity; educational attainment; health and survival; and political empowerment. Scarily, pandemic disruptions and a weak recovery means it’s now going to take another 132 years to close the global gender gap.
LinkedIn partners with WEF on the report — our unique data highlights a number of challenges facing working women and what we can do to make workplaces and societies more equal. Here’s what the data says.
Working Women Face Systemic Challenges
First, the bad news.
We saw clearly during the pandemic that women’s careers are more vulnerable to systemic shocks, and women pay a high price when there are economic upsets. That is particularly concerning when we consider what may lie ahead.
During the pandemic, female-dominated service industries like retail and hospitality bore the brunt of national lockdowns. Meanwhile, many women bore the double burden of work and caregiving, and were forced to step back from the workplace altogether. Not nearly enough employers stepped in to meet them halfway and offer the flexibility they needed.
LinkedIn’s data, featured in the gender gap report, also shows that the world has a gender imbalance in leadership roles in almost every country and industry. Women are severely under-represented in leadership, holding less than a third of leadership positions globally. There is a narrow pipeline of female talent that shrinks with seniority.
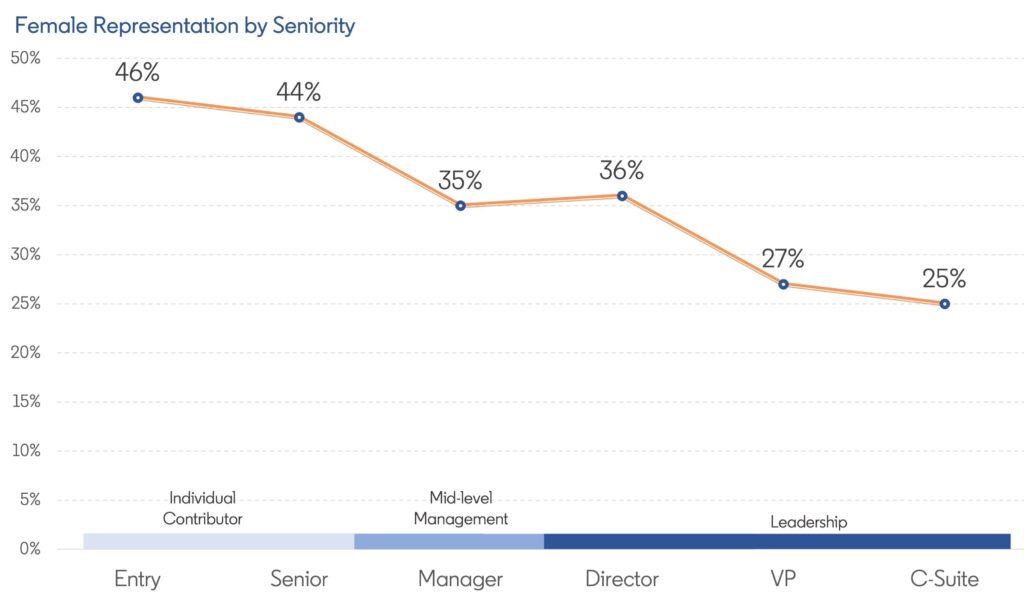
What is equally concerning is that LinkedIn’s new data reveals men have a significantly higher chance of being promoted into leadership roles than their female colleagues. Comparing the global average for men and women in 2021, men were 33% more likely to receive an internal leadership promotion than women. In countries like the Netherlands and Spain, men are 69% and 65% more likely to get promoted internally.
It’s very clear that women are facing systemic challenges in the workplace, preventing them from achieving full and equal participation in the labor market.
COVID-19 Has Contributed to a Rise in Female Founders
The gender gap report’s data paints a difficult picture of working women and their ability to make it to the top, but there was another trend in LinkedIn data that particularly stood out: a surge in female founders.
Women are starting their own businesses at a faster rate than men, with a marked increase during 2020. Globally, the share of founders grew by 45% in 2020 for women and by 32% for men, compared to the previous year, an acceleration of a longer-term labor market trend.
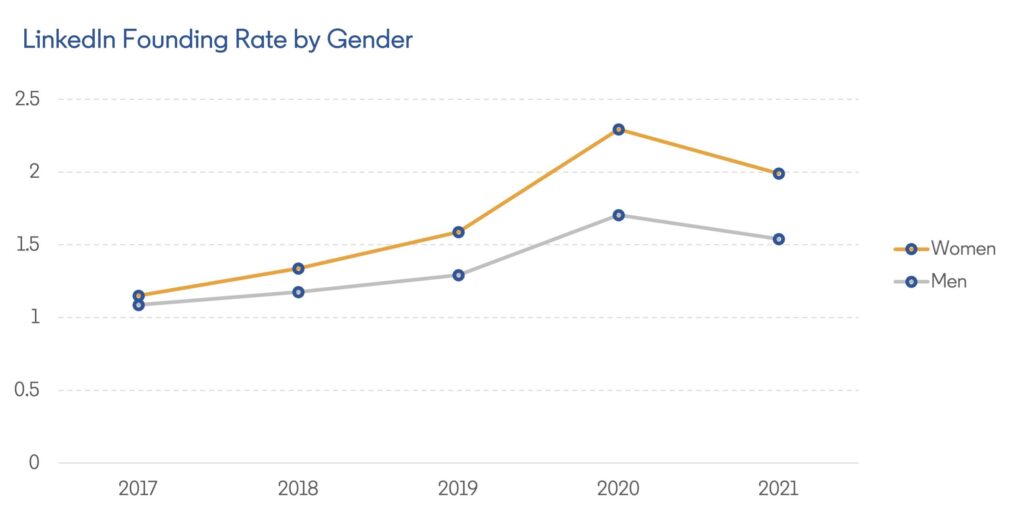
Why did so many more women choose to start a business — which would be daunting enough in normal times — during all the uncertainty and instability of a global pandemic?
While some undoubtedly started businesses to pursue long-held passions, many in this period likely became “necessity entrepreneurs”. In the face of economic headwinds and inequitable workplaces, these female founders sought to take more control of their careers — fueled by a need for income, for greater flexibility or because of a lack of opportunities at work.
Ultimately, we don’t know enough yet to say if this trend is a good or a bad thing for women. We uncovered some truly inspiring stories of resilience and entrepreneurialism as women struck out on their own. But we need to face the fact that many likely had their hand forced by inequitable working structures. At LinkedIn, we will continue to monitor this trend so that we can better understand its impact on women and the labor market.
With LinkedIn data showing women are 24% more likely than men to apply to remote roles, we need to make flexible working the norm for everyone if we want a diverse pool of talent.
There is some better news: The data shows that progress is possible, but it is happening extremely slowly. Women have been hired into leadership roles in increasing numbers since 2016. While progress stalled during the pandemic — with the annual share of women hired into leadership positions holding at 35% between 2019 and 2020 — it increased to 36% in 2021 and 37% in 2022. While the numbers are going in the right direction, it’s from a low base, and we’re not going anywhere near fast enough to make a meaningful difference.
Targeted Action Is Needed to Address the Global Gender Gap
The data is deeply troubling on many levels. But it also shines a light on where improvements can be made.
What can we do to solve the disproportionate challenges facing working women and turn the tide on the inequality that prevents them from participating fully in the global economy?
We know that the problems are systemic — which means we need a systemic response. Urgent, targeted action is needed to make workplaces fairer and more equal. Governments and businesses need to go further, faster, to help women overcome the imbalance that they face every day. There are three key areas where we must do more: inclusive hiring, internal mobility and flexibility.
We need to take a hard look at hiring practices, which must be inclusive and fair. Practical steps include removing bias from job descriptions, including women on interview panels and having representative candidate shortlists.
There should be more support for women’s internal mobility and progression. This means creating targeted mentoring and training programs for women — in particular at the pre-manager level — and increasing awareness about unconscious bias within organizations.
And with LinkedIn data showing women are 24% more likely than men to apply to remote roles, we need to make flexible working the norm for everyone if we want a diverse pool of talent. To help people find the job that suits their needs, LinkedIn has introduced dedicated filters for remote, hybrid and on-site roles.
A version of this piece originally appeared in the World Economic Forum.





