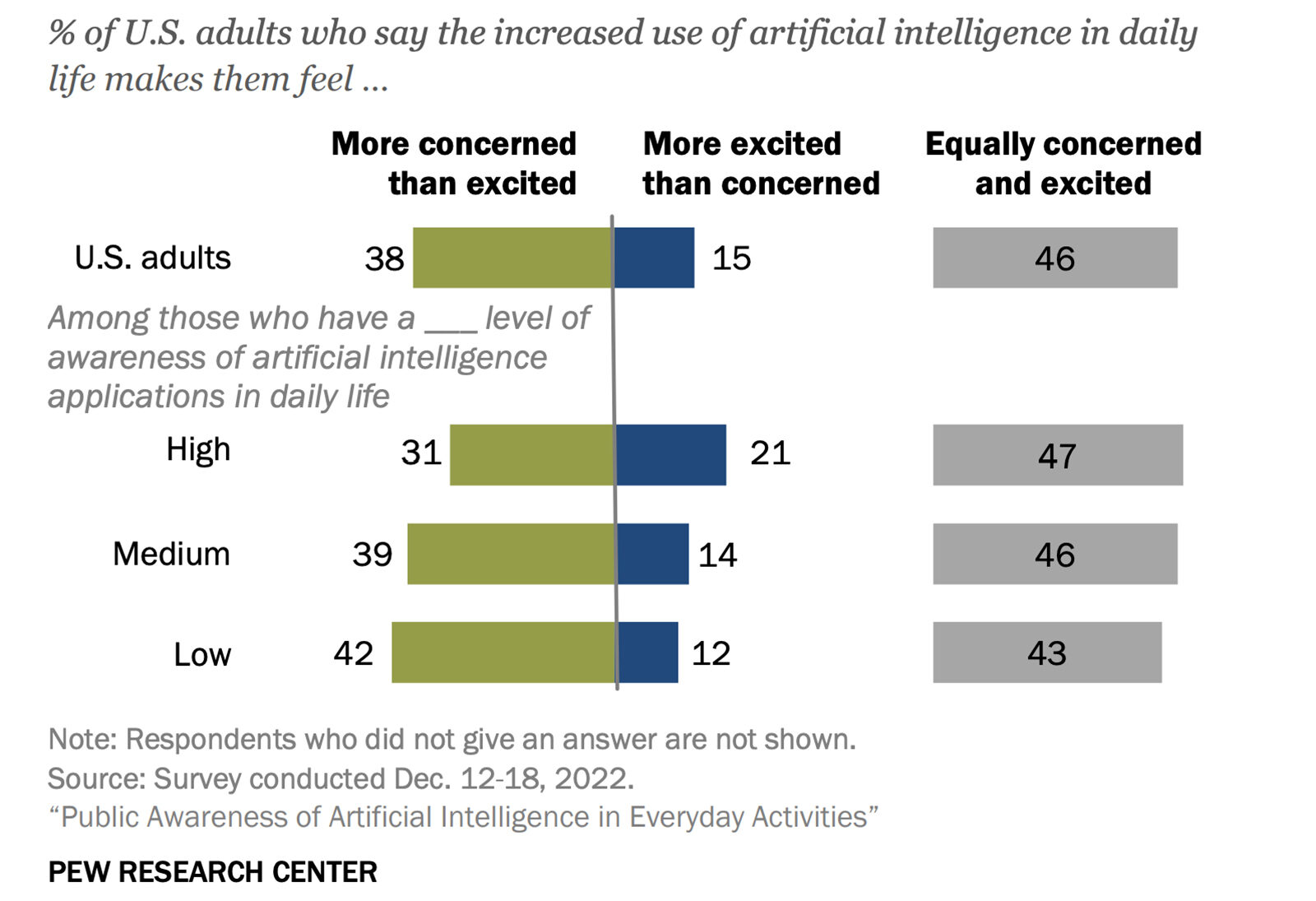
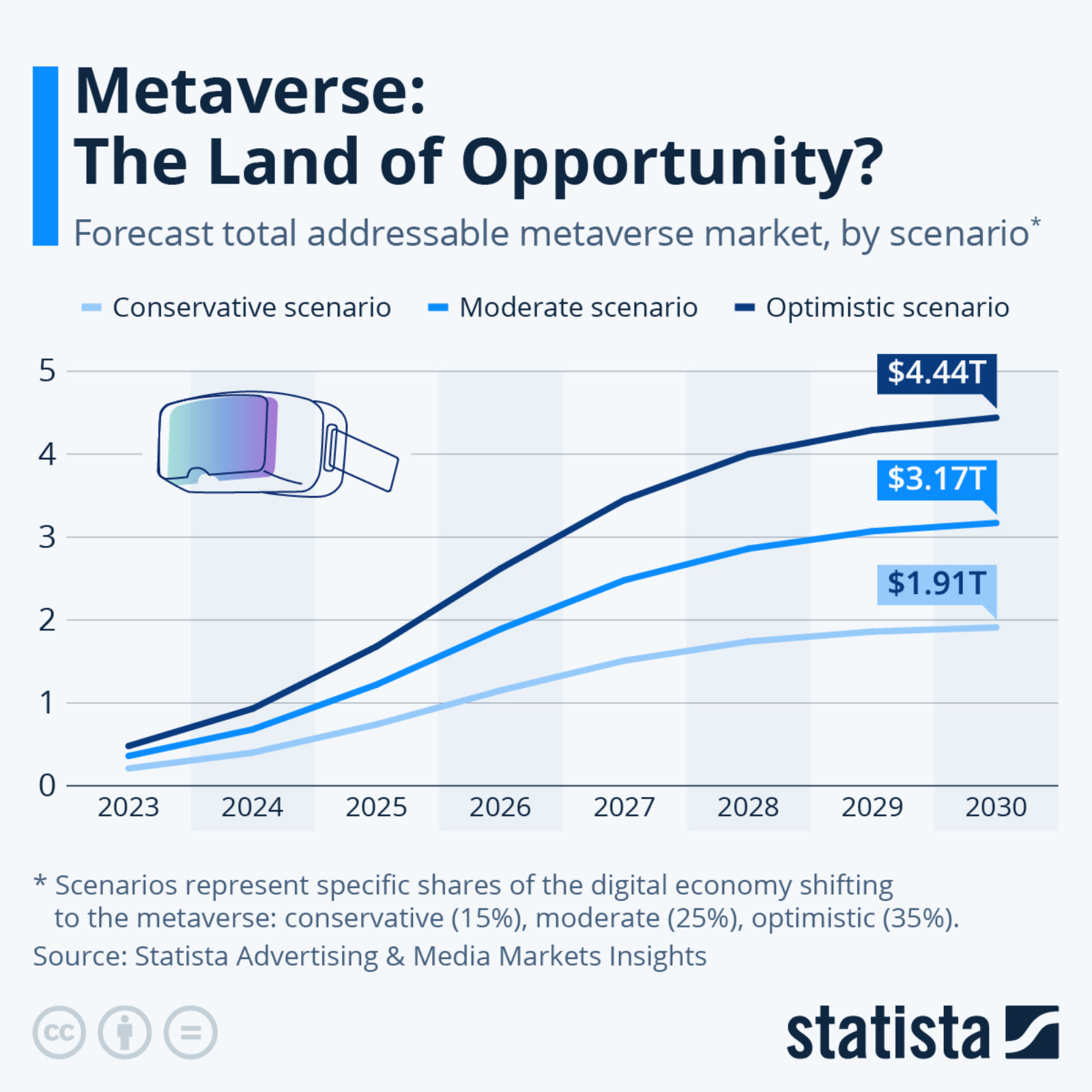
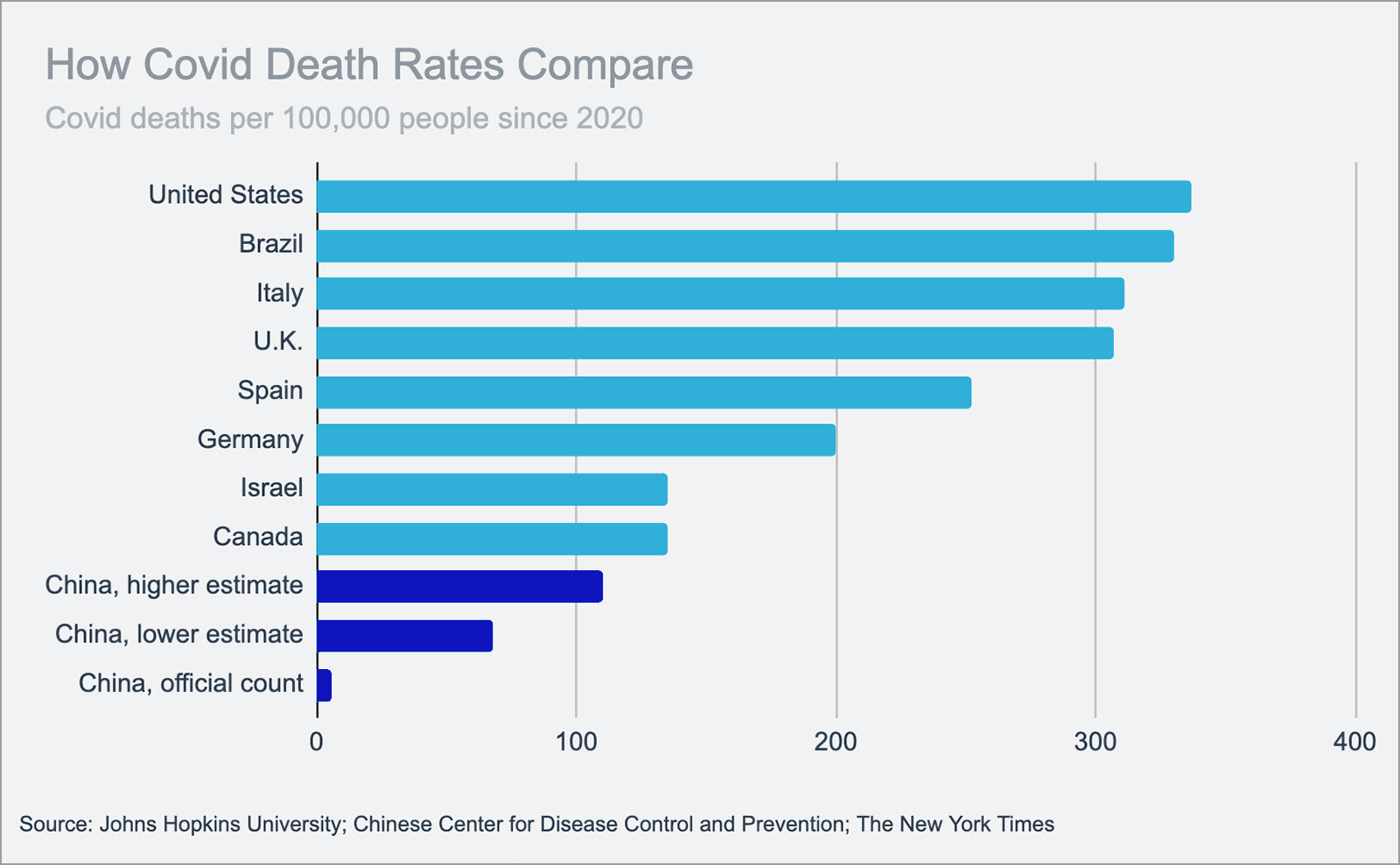
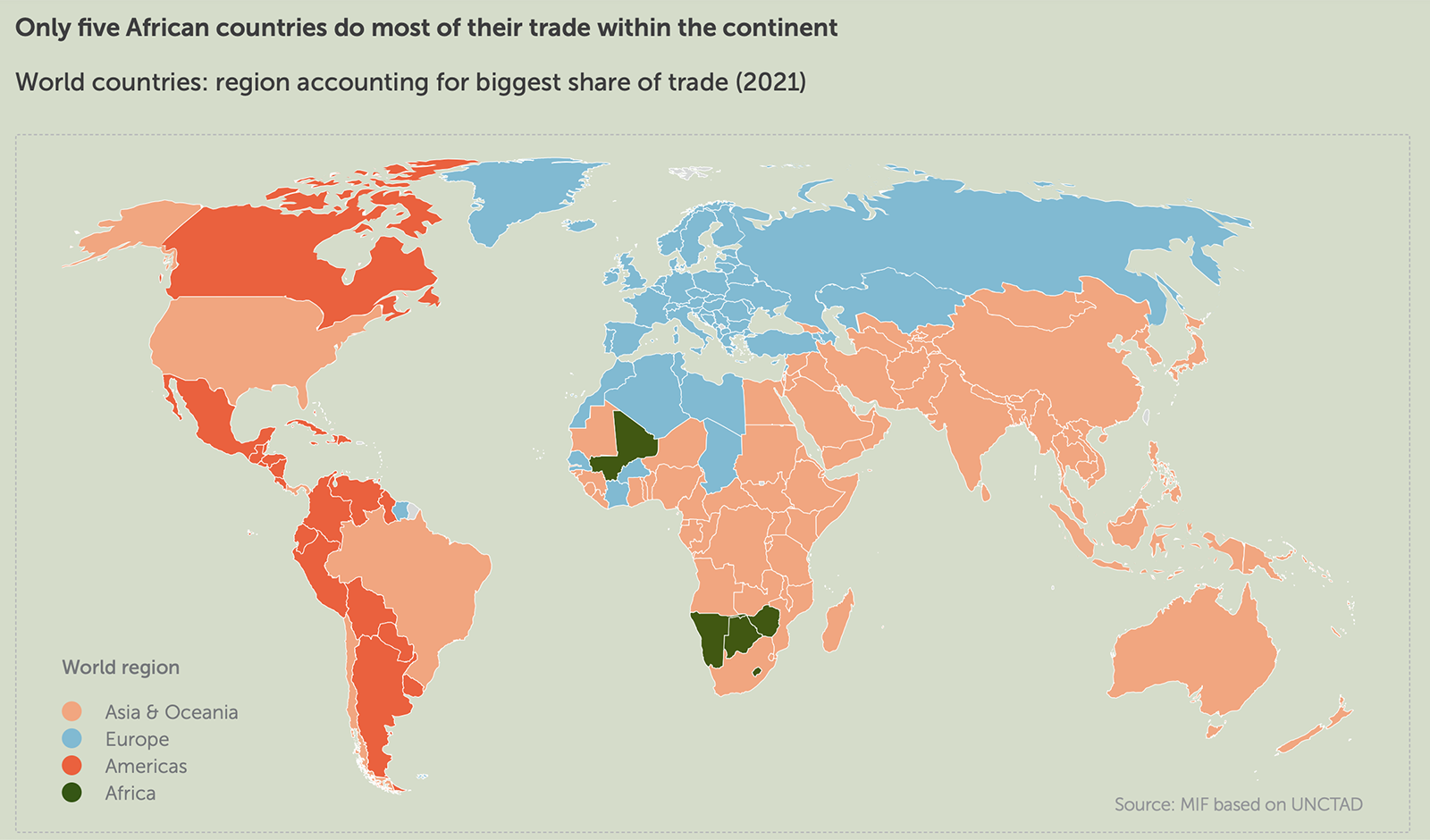
Rise in Fossil Fuel Emissions Slowing Worldwide
Source: The Economist
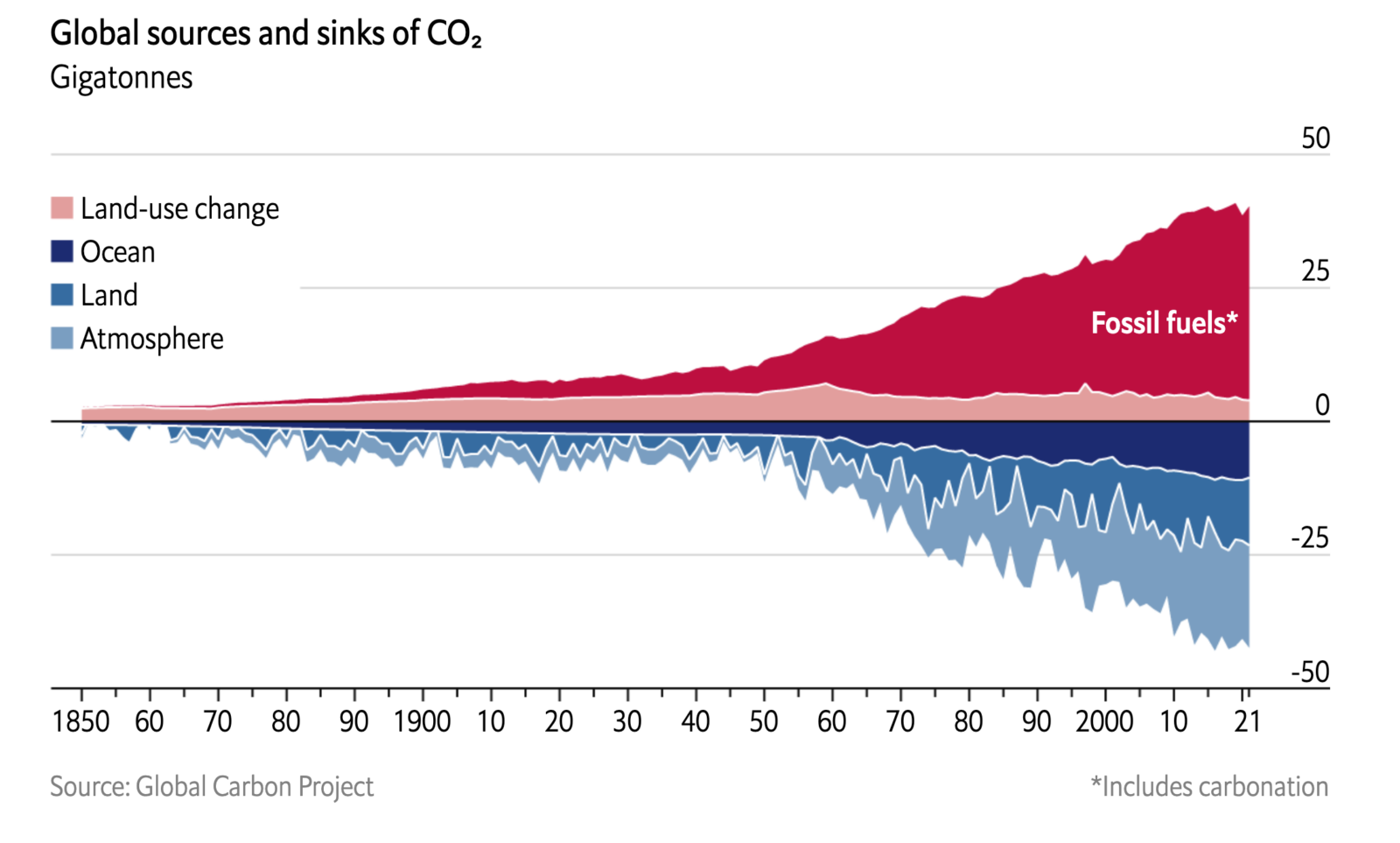
The growth in fossil fuel emissions is slowing down worldwide as countries make some progress in the fight against climate change. The rate of increase in global CO2 emissions has slowed from 3% per year in the 2000s to 0.5% per year in the last decade, reports the Global Carbon Project.
Part of the decline is due to a change in the global economy, in which GDP growth is less energy intensive — and therefore produces less carbon emissions (e.g., economies that move from manufacturing to services). In the last decade, 24 countries have decreased their carbon emissions while growing their economies, including countries across Europe, the Americas and Asia. Less-developed countries are also producing less carbon emissions as they use fossil fuels more efficiently than countries in the past. For example, India and Vietnam are greener than China, even though they are primarily powered by coal.
Another factor is an increased use of renewable energy and electric vehicles, according to the International Energy Agency. Solar and wind power were the leading sources of renewable energy and grew faster than any other energy source in 2022. But global coal use is also expected to increase, led by demand in Asia and countries looking for alternatives to high natural gas prices.